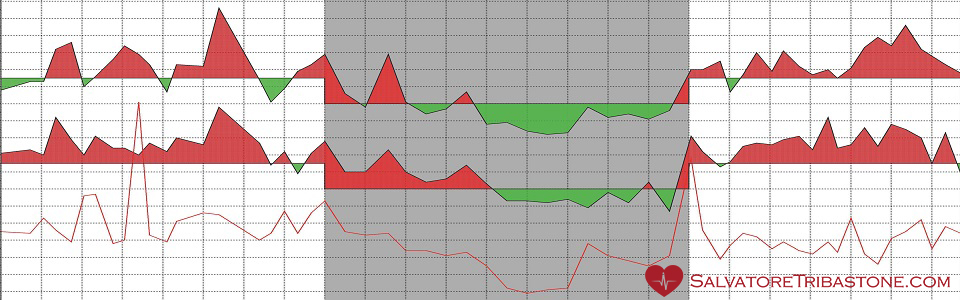
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring
ABPM helps evaluate blood pressure trends during normal daily activities and sleep for 24 hours

ABPM helps evaluate blood pressure trends during normal daily activities and sleep for 24 hours
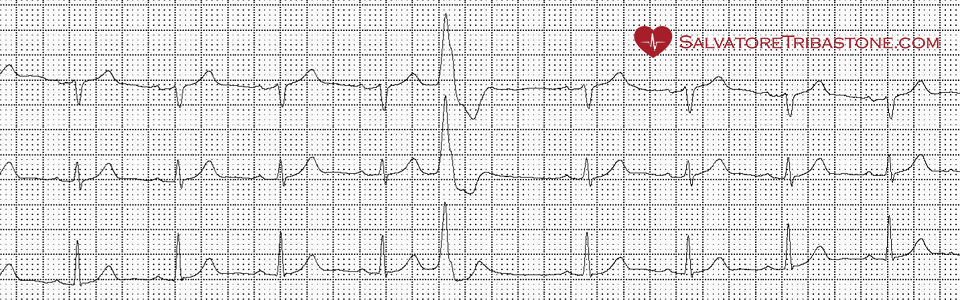
Holter ECG is used to detect heart rhythm abnormalities that may not appear during a standard ECG, which records only a few seconds.


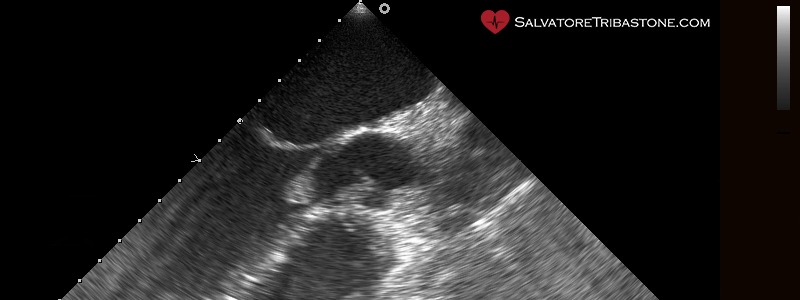
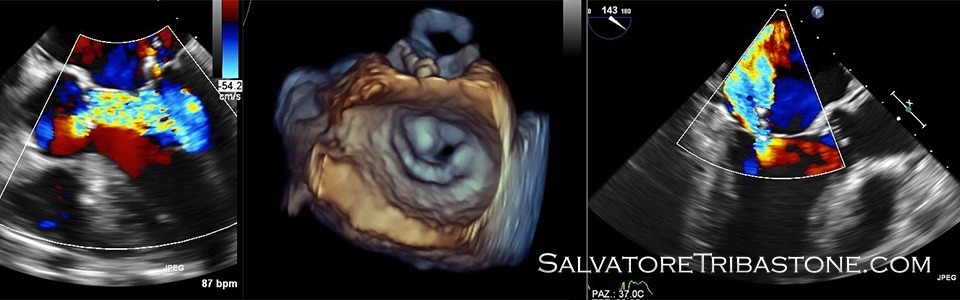
Echocardiography is a non-invasive test, which through the use of ultrasound in a frequency range of 2 to 10 MHz allows us to explore the anatomy and function of the heart. The exam consists of several phases (one-dimensional, two-dimensional, three-dimensional, doppler and colordoppler analysis) which together provide complete information allowing to perform detailed measurements and analysis of cardiac structures.